Methane Synthesis Test Facility for Effective Utilization of CO2 Completed and Commissioning Started for Full-scale Operation
After commissioning, a series of tests and continuous operation will be conducted by the end of fiscal 2019
As part of a project to develop effective carbon dioxide (CO2) utilization technologies, the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) has been working with INPEX Corporation and Hitachi Zosen Corporation. They have now completed construction of a test facility for synthesizing methane from CO2 and hydrogen at the Koshijihara Plant of INPEX’s Nagaoka Field Office in Nagaoka City, Niigata Prefecture. After commissioning, a series of tests and continuous operation will be conducted by the end of fiscal 2019.
The organizations aim to use this test facility to develop methanation technology, which is one of carbon recycling technologies. They will produce methane through synthesis of the CO2 generated at the Koshijihara Plant during the natural gas production process, together with hydrogen produced through electrolysis of water. Later, they will also evaluate and examine technical issues, including how to optimize the methane synthesis process, through a series of tests and continuous operation.
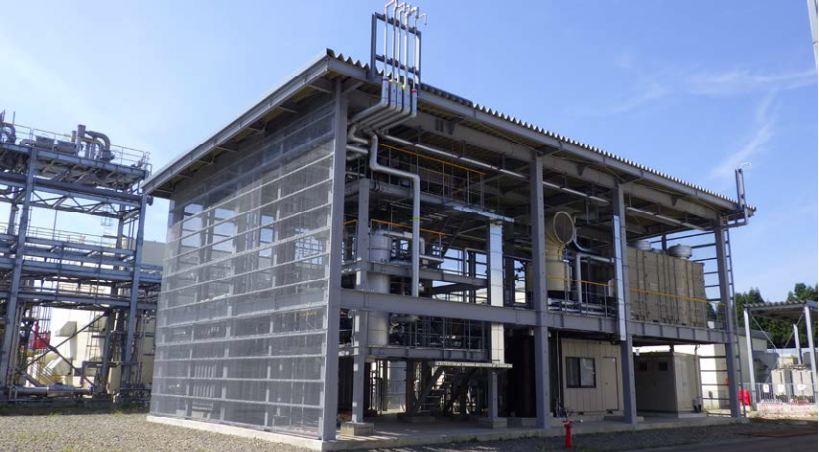

Figure 1. Methanation test facility
1. Overview
Reducing CO2 emissions from thermal power generation and other processes is an important climate change countermeasure. There is also a need to develop technologies that effectively utilize CO2 as a resource. Reuse of CO2 as fuels, chemical feedstock and other valuable materials is considered a useful way of efficient CO2 usage. Methane, the main component of natural gas (or town gas), holds great potential as an energy carrier*1, and because existing infrastructure for natural gas can be employed directly, it offers significant benefits.
According to this background, there are high expectations at the moment for practical application of methanation, which is the process of utilizing CO2 as a material in the production of methane. Methanation is a technology for synthesizing methane through a chemical reaction in a reactor containing a catalyst with CO2 from thermal power plants and other sources, which has been separated and captured, and hydrogen produced through electrolysis of water or other methods. Because CO2 emitted during combustion of methane can be offset against separated and captured CO2, if renewable energy can be used in the future to produce hydrogen through electrolysis of water, then the process might be able to dramatically reduce CO2 emissions.
NEDO is implementing a project*2 to develop technologies for effective utilization of CO2. Working with INPEX Corporation and Hitachi Zosen Corporation, the organizations have now completed construction of a test facility for synthesizing methane from CO2 and hydrogen at the Koshijihara Plant of INPEX’s Nagaoka Field Office in Nagaoka City, Niigata Prefecture. After commissioning, they will conduct a series of tests and continuous operation by the end of fiscal 2019.
At this test facility, the organizations will produce methane through synthesis of the CO2 generated at the Koshijihara Plant during the natural gas production process, together with hydrogen produced through electrolysis of water.
Through later full-scale operation, they aim to evaluate and examine technical issues, including how to optimize the methane synthesis process by varying a range of parameters including reaction temperature, reaction pressure and reaction loads, and to develop methanation technology, which is one of carbon recycling*3 technologies.
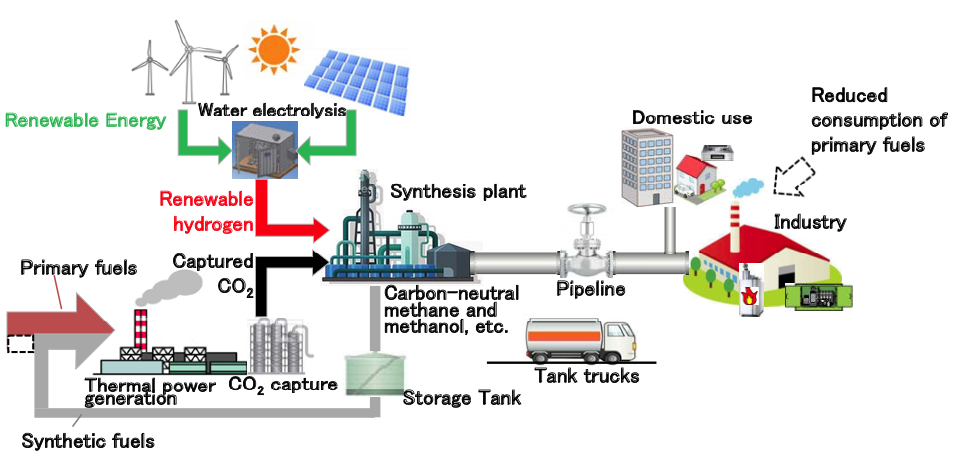
Figure 2. Overall flow of a future effective CO2 utilization system
2. Test facility overview
For methane synthesis, the test facility uses a Hitachi Zosen plate reactor that achieves highly efficient heat recovery (figure 3). As the world’s first trial using actual CO2 in a plate reactor, this initiative is focused on use of larger facilities in the future. This test facility has a methane synthesis capacity of 8 Nm3 per hour
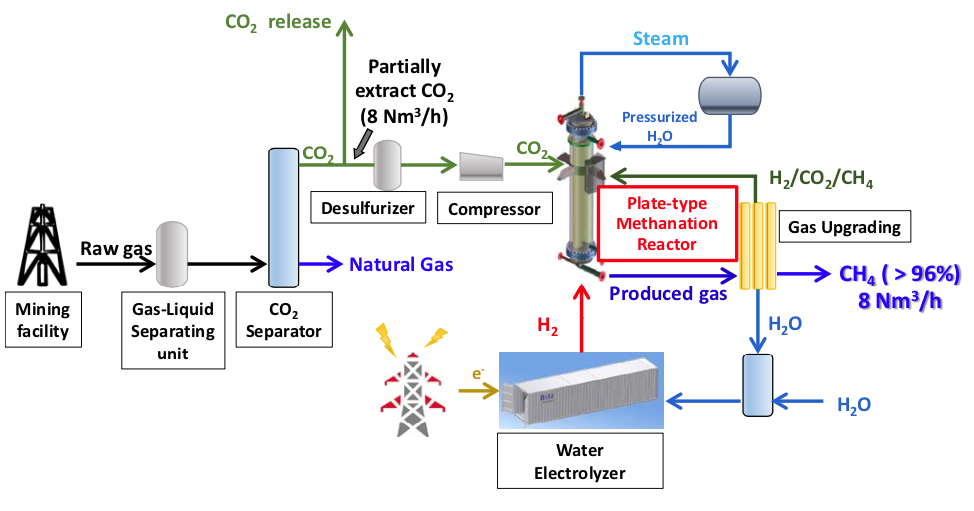
Figure 3. Plant conceptual diagram
3. Future plans
After commissioning, a series of tests and continuous operation will be conducted by the end of fiscal 2019. Technical issues will be examined and evaluated, and further improvements in capacity of the methane synthesis facility will be considered.
*1 Energy carrier: A chemical substance for carrying and storing energy.
*2 Project details:
Name: Development of next-generation thermal power generation technologies / Development of basic technologies for next-generation thermal power generation / Development of CO2 utilization technology project
Period: FY2017–2019
Scale: Approx. 1.39 billion yen (through full period)
*3 Carbon recycling: Separating and capturing CO2 as a resource and reusing it as a raw material or fuel through mineralization, artificial photosynthesis or methanation while restricting release of CO2 into the atmosphere.
Source: INPEX, press release, 2019-10-16.
