The Use of Food and Feed Crops for Bio-based Materials and the Related Effects on Food Security – Recognising Potential Benefits
Renewable Carbon Initiative Publishes New Insights into a Hotly Debated Topic and Urges for Careful and Evidence-based Debates
In 2023, the world faces a global hunger crisis. According to the World Food Programme“ a record 349 million people across 79 countries are facing acute food insecurity – up from 287 million in 2021. This constitutes a staggering rise of 200 million people compared to pre-COVID-19 pandemic levels. More than 900,000 people worldwide are fighting to survive in famine-like conditions. This is ten times more than five years ago, an alarmingly rapid increase”.
Against this backdrop it may seem misanthropic to publish a paper challenging the widely held view that the use of food and feed crops for anything other than food and feed uses – namely, for bio-based chemicals and materials – is detrimental to food security. However, RCI’s new publication aims to show that the well-known biomass debate is flawed, subjective and not fully based on evidence – and as a result, distracts from much more powerful causes of hunger in the world. These are to a large extent climate change, conflict, extreme inequalities in wealth distribution, heavy dependence on food imports from industrial countries, overconsumption of meat, losses along the value chain and the impact of the COVID pandemic, according to the World Food Programme in 2023. Competition between biomass uses is not mentioned among the relevant causes.
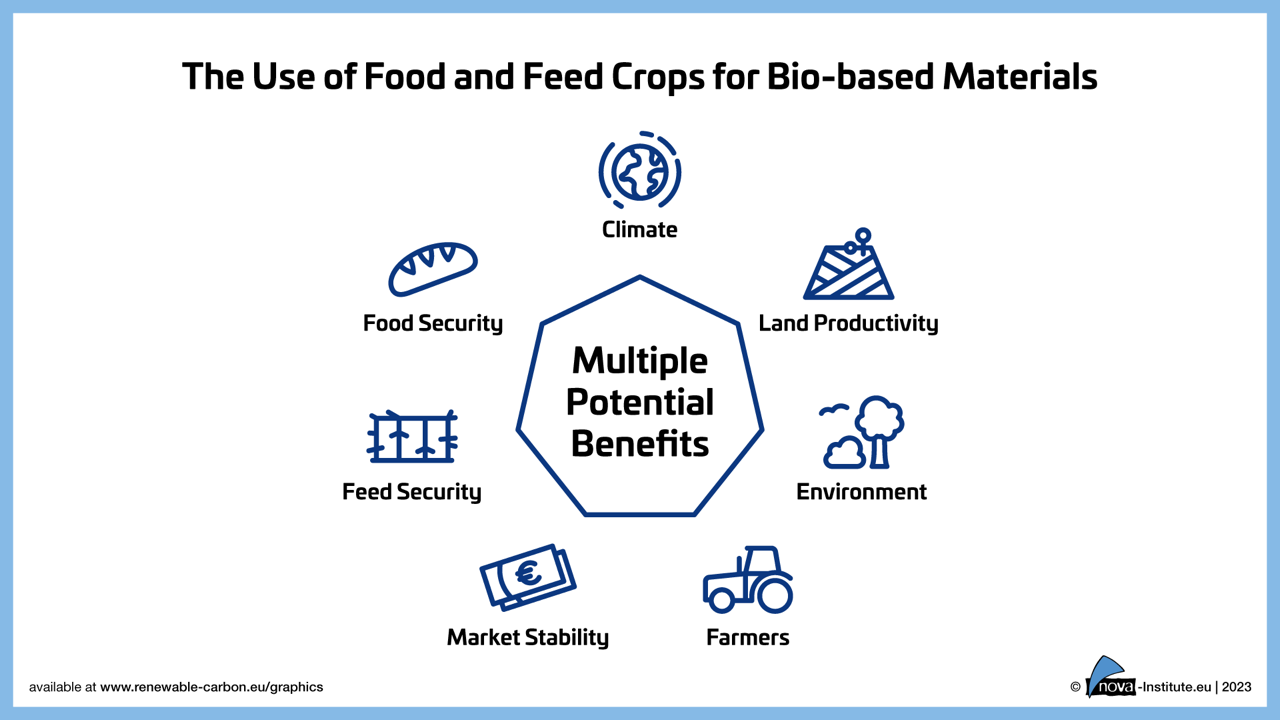
The use of biomass for industrial applications, on the other hand, has the potential to replace fossil feedstocks and thus contribute to the urgently needed reduction of fossil carbon emissions into our atmosphere to mitigate climate change. While not denying the dire need to combat world hunger, the authors of the paper argue that using food and feed crops for chemicals and materials will not necessarily exacerbate food insecurity, and in fact has the potential to cause multiple benefits for local and global food security, climate mitigation and other factors:
- The climate wins. There is a need to shift away from fossil feedstocks to achieve climate change mitigation. Bio-based materials are part of the solution and can thus help to mitigate one of the leading causes of hunger in the world.
- Land productivity wins. The competition between applications is not for the type of crop grown, but for the land. The overall availability of arable land, and therefore food and feed on the planet determines what is possible and what is not. Food and feed crops offer high yields through long-term optimisation and a variety of co-products used simultaneously in a variety of applications, making the most out of the available land.
- The environment wins due to increased resource efficiency and productivity of food and feed crops and the reduced land area, especially if agricultural practices are improved to better respect soil health and ecosystems.
- Farmers win because they have more options for selling stock to different markets (food, feed, biofuels, material industry) and therefore more economic security. This can increase investment and ultimately the availability of arable land and ensure sustainable rural development to maintain EU agriculture.
- Market stability wins due to increased global availability of food and feed crops, reducing the risk of shortages and speculation peaks. The influence of biofuels and biobased materials on food prices is negligible.
- Feed security wins due to the high value of the protein-rich co-products of food and feed crops (which can also be used to supply protein for human nutrition).
- Food security wins due to the increased overall availability of edible crops that can be stored and flexibly distributed in times of crisis (emergency reserve), actually mitigating risks of supply-cycle triggered regional hunger events.
The authors argue that “the bigger picture is not the specific issue of whether food or nonfood crops are being used to produce biomaterials, but rather the integration of any feedstock for biomaterials production into a landscape and its social, environmental, and pricing effects there” (BFA 2022). The choice of feedstock in any given case depends on many factors and is site specific. There is no “one-size-fits-all” solution.
All in all, this complex topic requires in-depth and detailed analyses, and simplified claims will not do it justice. In the worst case, simple claims will only distract from the real causes of hunger in the world and at the same time prevent a young and innovative industry from fulfilling its potential of contributing to climate change mitigation and offering more sustainable materials. The Renewable Carbon Initiative encourages comprehensive discussions that balance the need for food security with the potential benefits of bio-based materials derived from food and feed crops.
You can download the short version here:
https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/product/rci-paper-on-the-use-of-food-and-feed-crops-for-bio-based-materials-and-the-related-effects-on-food-security-recognising-potential-benefits-short-version-pdf/
The long version is available via
https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/product/rci-paper-on-the-use-of-food-and-feed-crops-for-bio-based-materials-and-the-related-effects-on-food-security-recognising-potential-benefits-long-version-pdf/.
Disclaimer
RCI members are a diverse group of companies addressing the challenges of the transition to renewable carbon with different approaches. The opinions expressed in this press release may not reflect the exact individual policies and views of all RCI members. The Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI), founded in September 2020, is a group of more than 50 pioneering companies from the entire chemical value chain from raw material to end-of-life. The aim of the initiative is to support and speed up the transition from fossil carbon to renewable carbon from biomass, direct CO2 utilisation or recycling for all organic chemicals and materials
Source:
Renewable Carbon Initiative, press release, 2023-06-14.
