ESA approves Norwegian Full-Scale Carbon Capture and Storage: up to €2.1bn in aid to meet climate goals
Norwegian government together with the European Commission to support the project "Northern Lights"
The CCS Full-Scale project is a central part of Norway’s efforts to reduce its carbon footprint and meet the European goal of climate-neutrality by 2050. It is the largest single state aid award ever approved by the EFTA Surveillance Authority (ESA).
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) has been recognised by the European Union as key to reducing the harmful environmental effects of carbon-intensive sectors (such as construction), where emissions are difficult to avoid.
By supporting the project, the Norwegian government aims to facilitate further scaling up of CCS globally, by sharing knowledge and experience. The project will establish infrastructure for capture, transport and storage of CO2 emissions that can pave the way for future investments, innovation and technology in CCS as a climate-change mitigation tool.
“This CCS project is a groundbreaking step towards tackling climate change – an issue that affects all of us. Protecting the environment is at the heart of the European agenda, and ESA is pleased to work with Norway and the European Commission to find ways to support this important goal”, said Bente Angell-Hansen, President of ESA.
The approved project would allow for the establishment of carbon capture facilities at Norcem, a cement factory in Brevik, and Fortum Oslo Varme, a Waste-to-Energy plant. The captured CO2 is then to be transported and stored deep below the seabed in the North Sea. This part of the process is to be carried out by a joint venture between Shell, Total and Equinor, known as Northern Lights.
The Full-Scale CCS Project promises to become the first of its kind to go live in Europe. It has a budget of up to EUR 2.57 billion (NOK 27.6 billion), which will cover construction and 10 years of operation. The Norwegian government would cover around 80% of the project’s estimated budget.
The measure was formally notified on 2 July 2020. Today, ESA concludes that the measure is in line with EEA state aid rules. set out in Article 61(3)(c) of the EEA Agreement.
ESA’s decision will be published once confidentiality has been cleared.
More information
CCS Technology
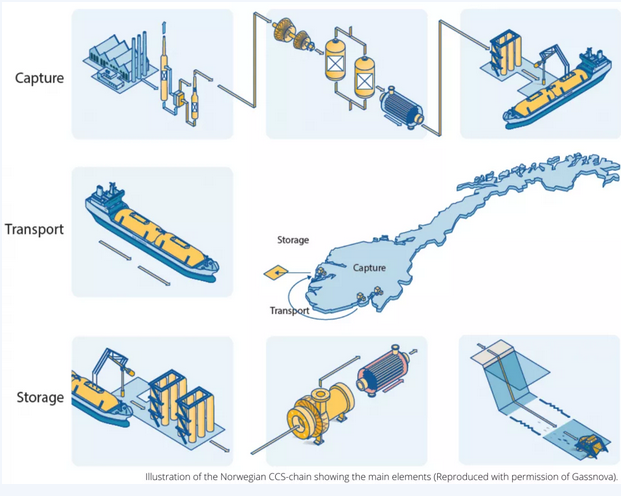
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is an integrated chain of technologies designed to capture CO2 emissions from industrial installations.
It involves three main steps:
1) CO2 is captured at the emission source.
2) The captured CO2 is compressed and transported to a carefully selected and safe storage site.
3) The compressed CO2 is injected deep underground into a rock formation and stored there permanently.
Norwegian and European climate goals
CCS is a key part of Norway’s strategic aim to transform energy intensive industries, which make up around 25% of global CO2 emissions, into sustainable industries long-term.
In response to urgent climate and environmental challenges, the European Union launched The European Green Deal in December 2019. This is a comprehensive reform program that aims to make the EU economy environmentally sustainable.
Its central goal is zero emissions of greenhouse gases in the EU by 2050. The Deal aims to make climate neutrality legally binding: all EU policies should be in line with the goal of an economy with net-zero greenhouse gas emissions in 2050.
EU Member States are required to present long-term strategies on how they plan to reduce their emissions. Norway is closely connected to the EU through the EEA Agreement, and is committed to making joint environmental efforts in line with the EU goal. Norway intends to share the knowledge generated by this project across European industries.
Source: ESA, press release, 2020-07-17.
